Currently Empty: £0.00
Technology
Understanding Soil Bearing Capacity in Simple Terms
🚀 1. Introduction
Soil bearing capacity is the MVP of geotechnical engineering. It’s all about how much weight the soil can handle without buckling or sinking too much. Getting this right is key to building safe, wallet-friendly foundations for houses, bridges, and beyond.
🧐 2. What is Soil Bearing Capacity?
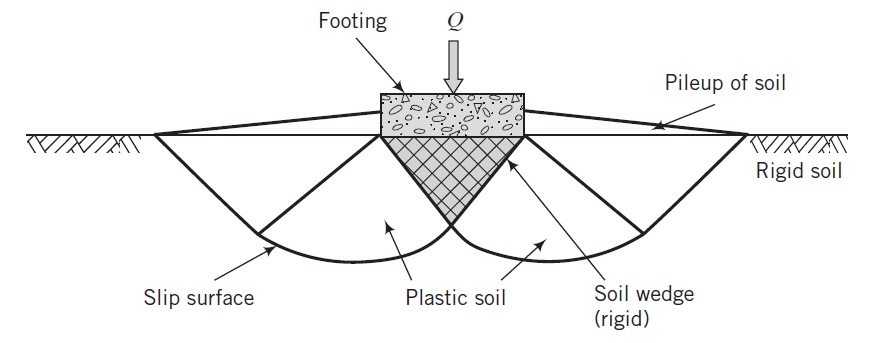
Soil bearing capacity is the max load per unit area the soil can take before it cries uncle. Think of it in kPa (kilopascals) or psf (pounds per square foot)—it’s the soil’s power limit!
📊 3. Types of Bearing Capacity
- Ultimate Bearing Capacity (q_u) – The absolute max pressure before the soil taps out.
- Safe Bearing Capacity (q_s) – The chill limit after tossing in a safety cushion.
- Allowable Bearing Capacity (q_a) – The sweet spot balancing safety and settlement vibes.
⚙️ 4. Factors Affecting Soil Bearing Capacity
Soil Type
- Rock and dense sand? Total champs. Clay or loose silt? Not so much.
Moisture Content
- Wet soil can turn weak, especially the fine-grained crew.
Depth of Foundation
- Deeper = stronger, thanks to more pressure and confinement.
Compaction and Density
- Tight, compacted soil > loose, messy soil. Always.
🔍 5. Methods to Determine Soil Bearing Capacity
- Standard Penetration Test (SPT): Hammer blows tell you how tough the soil is.
- Plate Load Test: Watches how soil reacts to a test load.
- Cone Penetration Test (CPT): A cone dives in and spills the resistance tea.
- Empirical Formulas: Terzaghi and Meyerhof drop equations to crunch the numbers.
📋 6. Typical Bearing Capacity Values for Different Soils
| Soil Type | Approximate Bearing Capacity (kPa) |
|---|---|
| Hard Rock | 2000 – 4000 |
| Dense Sand | 200 – 600 |
| Loose Sand | 50 – 200 |
| Stiff Clay | 100 – 300 |
| Soft Clay | 50 – 100 |
💪 7. Improving Soil Bearing Capacity
Got weak soil? No sweat—here’s how to level up:
- Compaction: Rollers and compactors pack it tight.
- Soil Stabilization: Mix in cement, lime, or magic potions for strength.
- Deep Foundations: Piles or piers send the load to tougher layers below.
- Grouting: Pump in goodies to glue the soil together and fill gaps.
🎉 8. Conclusion
Nailing soil bearing capacity is your ticket to picking the perfect foundation and keeping structures steady. With solid site investigations and some soil-boosting tricks, engineers can craft foundations that stand tall and proud for years! 🌍