Currently Empty: £0.00
Technology
Shallow Foundations Explained
🎯 1. Basics of Shallow Foundations
Shallow foundations are the unsung heroes of construction, transferring building loads to the ground with swagger—at a shallow depth, of course! These bad boys shine when strong soil layers chill near the surface. Economical, easy to build, and the go-to for residential, commercial, and industrial vibes.
🛠️ Types of Shallow Foundations
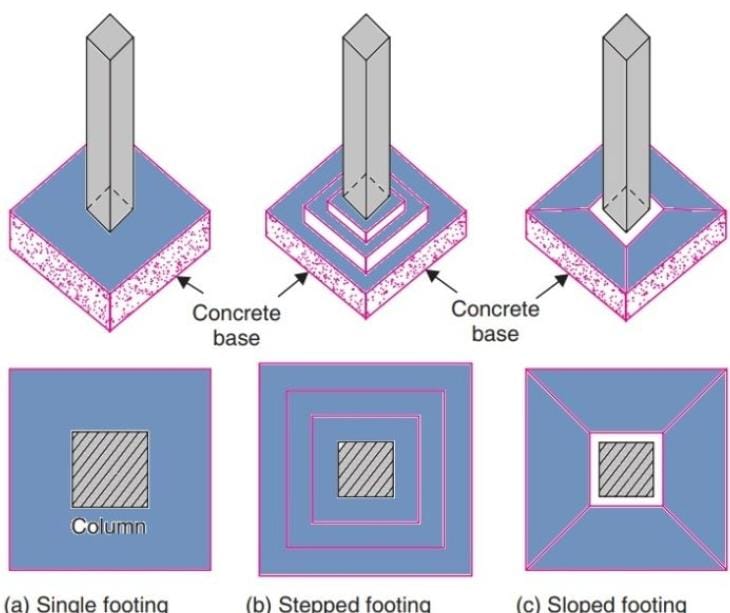
Spread Footings
- What they do: Hold up individual columns or walls like a boss.
- Superpower: Spreads the load over a bigger area.
- Where they flex: Residential homes and small structures.
Strip Footings
- What they do: Continuous support for rows of columns or walls.
- Perfect for: Load-bearing walls and framed setups.
- Cool trick: Distributes loads like a pro along the foundation.
Mat Foundations (Raft Foundations)
- What they do: Big slabs that flex over a massive area.
- When they shine: Low bearing capacity soils or high-rise beasts.
- Bonus: Kicks differential settlement to the curb.
🔥 When to Use Shallow Foundations
Shallow foundations are your VIPs when:
- The soil’s got bearing capacity near the surface.
- The structure’s light and not throwing heavyweight punches.
- Soil movement’s chill (no shrink-swell drama from clay).
- The groundwater table isn’t crashing the party.
- You want bang for your buck—less digging, less dough.
🧠 Design Considerations for Shallow Foundations
Bearing Capacity of Soil
- Mission: Stop shear failure in its tracks.
- Power tools:
- Standard Penetration Test (SPT)
- Plate Load Test
- Cone Penetration Test (CPT)
Settlement Control
- Goal: Keep differential settlement from wrecking the vibe.
- Mat foundations FTW: Even load distribution = less drama.
Depth of Foundation
- Sweet spot: 1.0-3.0 meters below ground level.
- Why: Dodges soil erosion and frost’s icy grip.
Groundwater Effects
- Challenge: High water table can nerf soil strength.
- Fix: Drainage systems + waterproofing = winning.
Load Distribution
- Key: Spread the love evenly to keep things stable.
- Engineer magic: Reinforcement + slick calculations.
💪 Advantages of Shallow Foundations
- Cost-Effective: Less digging, fewer materials—cha-ching!
- Easy to Construct: Simple moves, speedy builds.
- Efficient Load Transfer: Perfect for small-to-medium gigs.
- Lower Risk of Structural Failure: Nail the design, and it’s rock-solid.
⚠️ Limitations of Shallow Foundations
- Not for Weak Soils: Low bearing capacity? Call deep foundations.
- Groundwater Woes: High water table = shaky foundations.
- Seasonal Struggles: Expansive clays and frost heave can mess things up.
🎉 Conclusion
Shallow foundations are the MVPs of cost and construction ease. With killer soil investigation and smart design, they deliver stability and dodge disasters like settlement or failure. Know your soil, pick your type, and watch engineers craft structures that stand the test of time! 🚀